先備知識與注意事項
本篇文章將介紹在DAG(directed acyclic graph)上處理Single-Source Shortest Path問題之演算法,除了DAG之外,與之息息相關的Topological Sort也會跑出來,再加上Path-Relaxation Property,就能建構起本篇文章的演算法核心。
目錄
名詞概念回顧
DAG(directed acyclic graph)
所謂的DAG(directed acyclic graph),就是不存在cycle的directed graph,如圖一(a)與圖一(b):
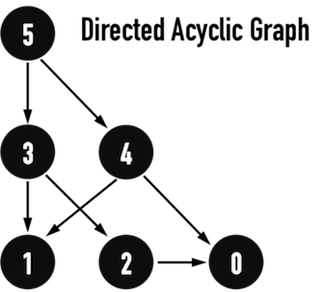
圖一(a)。

圖一(b)。
Topological Sort
若在DAG上,存在一條從vertex(X)指向vertex(Y)的edge(X,Y),那麼在Topological Sort中,vertex(X)一定出現在vertex(Y)之前。
(關於DAG與Topological Sort的詳細介紹與演算法,請參考Graph: 利用DFS尋找DAG的Topological Sort(拓撲排序)。)
試尋找圖一(a)之DAG的Topological Sort,如圖二(a)。可以確定的是,Topological Sort可能不唯一。
- 圖二(a)之Graph存在edge(4,1),因此在Topological Sort中vertex(4)一定在vertex(1)之前。依此類推,可以觀察其餘vertex在Topological Sort裡的相互關係。
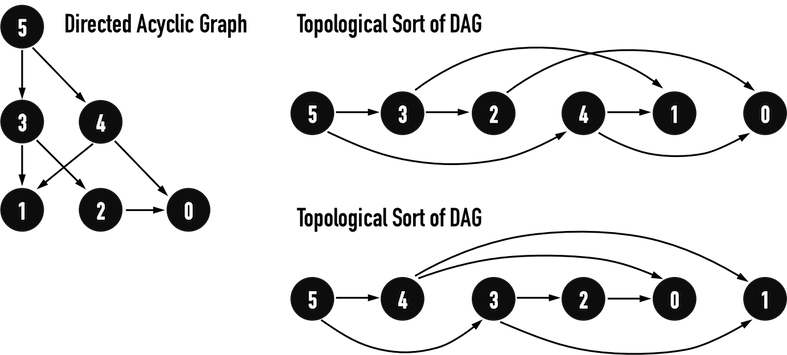
圖二(a)。
圖二(b)為圖一(b)之DAG的Topological Sort。
圖二(b)。
Path-Relaxation Property
根據Path-Relaxation Property:若從vertex(0)走到vertex(3)之最短路徑為\(Path:0-1-2-3\),那麼只要在對edge進行Relaxation的順序出現「edge(0,1)\(-\)edge(1,2)\(-\)edge(2,3)」的順序,不管其他edge(0,2)、edge(1,3)是否也有進行Relaxation,distance[3]一定能夠更新至最短路徑\(Path:0-1-2-3\)的weight,distance[3]\(=\delta(0,3)=w(0,1)+w(1,2)+w(2,3)\)。
(詳細定義請參考Single-Source Shortest Path:Intro(簡介)。)

圖三。
Single-Source Shortest Path in DAG
有了以上概念之後,要在DAG上找到Single-Source Shortest Path就變得輕鬆寫意了:
- 找到DAG的Topological Sort;
- 按照Topological Sort的vertex順序,對所有從該vertex出發連接至其餘vertex的edge進行Relaxation。
- 大功告成。
為什麼這樣可行?
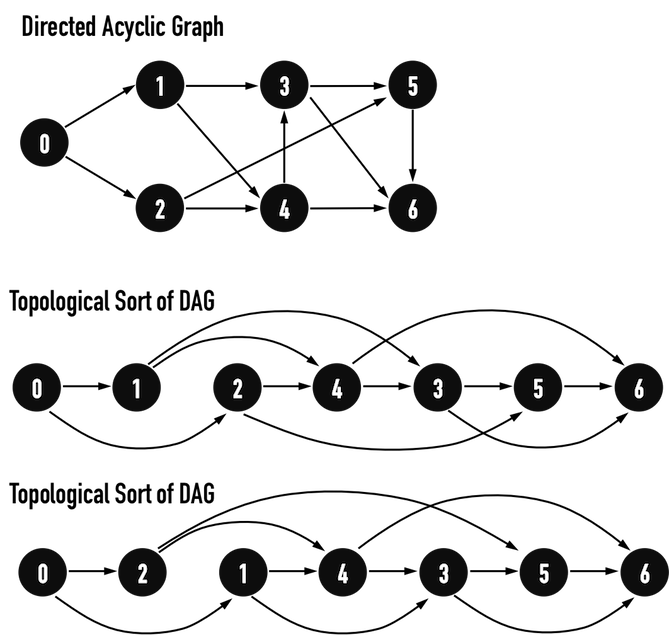
因為在DAG中,不存在cycle(若從vertex(X)離開後,就不可能再回到vertex(X)),所以路徑只有「一個方向」,因此最短路徑的方向一定也依循著DAG的「大方向」。以圖四(a)為例,DAG的「大方向」即為「由左至右」,從vertex(0)至vertex(6)。
而Topological Sort會把vertex按照「大方向的頭到尾」之順序排列,若按照此vertex順序,對所有與此vertex相連之edge進行Relax(),就會從最短路徑的最前端edge開始,一路往最短路徑之尾端edge進行Relax(),如此便滿足Path-Relaxation Property, 因此,以上演算法可以得到最短路徑。
圖四(a)。
以下便按照上述演算法,在圖四(a)之DAG上找到Single-Source問題之最短路徑,見圖四(b)-(g)。
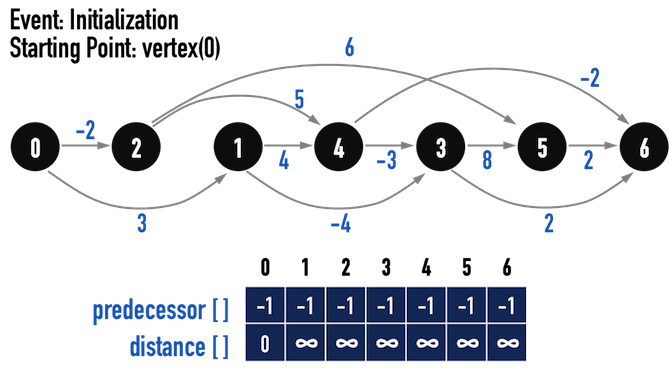
圖四(b)。
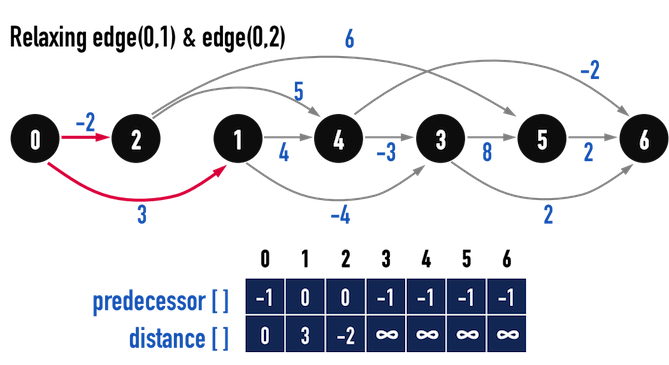
圖四(c)。
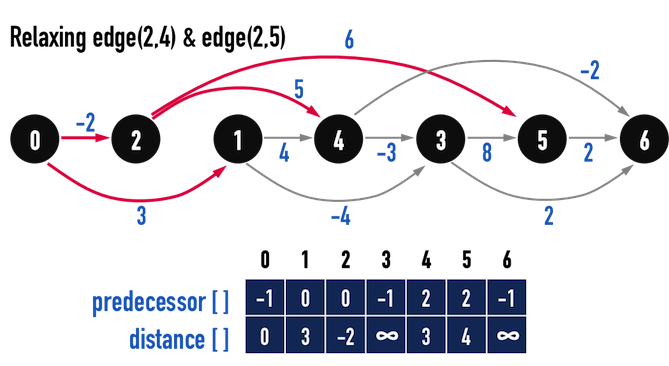
圖四(d)。

圖四(e)。
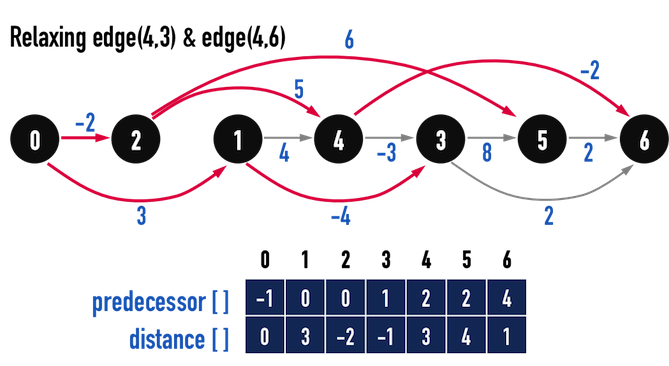
圖四(f)。
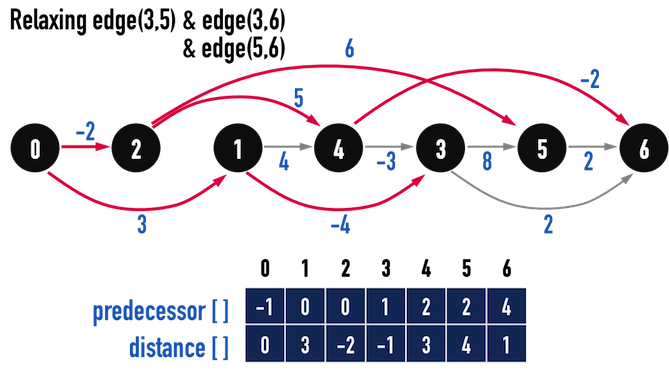
圖四(g)。
最後,由以上演算法找到的Predecessor Subgraph如圖四(h):
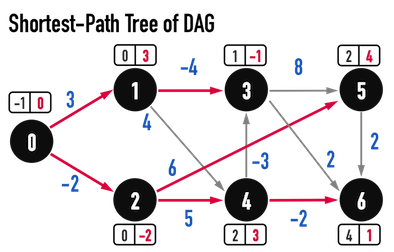
圖四(g)。
程式碼
範例程式碼中包含:
class Graph_SP:
- 基本的資料項目:
predecessor、distance、num_vertex、AdjList。 Relax()、InitializeSingleSource()之功能與Bellman-Ford Algorithm所使用相同。DAG_SP():尋找Shortest-Path Tree的主要函式,功能如前一小節所述。GetTopologicalSort():可以視為DFS()的變形,主要功能是建立color[]、discover[]、finish[]等資料項目,並把從DAG_SP()接收來的資料項目topologicalsort[]傳進DFSVisit_TS()。
順便在找到topologicalsort[]後,將discover[]與finish[]印出。DFSVisit_TS():此為DFSVisit()的變形,唯一修改的部分是在finish[]更新後,多加了一行array[count--] = vertex;,其中count為topologicalsort[]的index,用意是要按照「探索結束」的先後,將vertex依序從topologicalsort[]的尾端放到前端,如此一來,topologicalsort[]所存放的vertex,就會按照finish[]由大到小的順序。
以及main():建立如圖四(a)之AdjList,並進行DAG_SP()。
(關於DFS()與DFSVisit()之概念與程式碼,請參考Graph: Depth-First Search(DFS,深度優先搜尋)。)
(關於Topological Sort與DFS()的關聯,請參考Graph: 利用DFS尋找DAG的Topological Sort(拓撲排序)。)
// C++ code
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <utility> // for std::pair<>
#include <iomanip> // for std::setw()
const int Max_Distance = 100;
class Graph_SP{ // SP serves as Shortest Path
private:
int num_vertex;
std::vector<std::list<std::pair<int,int>>> AdjList;
std::vector<int> predecessor, distance;
public:
Graph_SP():num_vertex(0){};
Graph_SP(int n):num_vertex(n){
AdjList.resize(num_vertex);
}
void AddEdge(int from, int to, int weight);
void PrintDataArray(std::vector<int> array);
void PrintIntArray(int *array);
void InitializeSingleSource(int Start); // 以Start作為起點
void Relax(int X, int Y, int weight); // 對edge(X,Y)進行Relax
void DAG_SP(int Start = 0); // 需要 DFS, 加一個額外的Linked list
void GetTopologicalSort(int *array, int Start);
void DFSVisit_TS(int *array, int *color, int *discover,
int *finish, int vertex, int &time, int &count);
};
void Graph_SP::GetTopologicalSort(int *array, int Start){
int color[num_vertex], discover[num_vertex], finish[num_vertex];
for (int i = 0; i < num_vertex; i++) {
color[i] = 0;
discover[i] = 0;
finish[i] = 0;
predecessor[i] = -1;
}
int time = 0,
count = num_vertex-1, // count 為 topologicalsort[] 的 index
i = Start;
for (int j = 0; j < num_vertex; j++) {
if (color[i] == 0) {
DFSVisit_TS(array, color, discover, finish, i, time, count);
}
i = j;
}
std::cout << "\nprint discover time:\n";
PrintIntArray(discover);
std::cout << "\nprint finish time:\n";
PrintIntArray(finish);
}
void Graph_SP::DFSVisit_TS(int *array, int *color, int *discover,
int *finish, int vertex, int &time, int &count){
color[vertex] = 1; // set gray
discover[vertex] = ++time;
for (std::list<std::pair<int,int>>::iterator itr = AdjList[vertex].begin();
itr != AdjList[vertex].end(); itr++) {
if (color[(*itr).first] == 0) {
predecessor[(*itr).first] = vertex;
DFSVisit_TS(array, color, discover, finish, (*itr).first, time, count);
}
}
color[vertex] = 2; // set black
finish[vertex] = ++time;
array[count--] = vertex; // 產生Topological Sort
}
void Graph_SP::DAG_SP(int Start){
InitializeSingleSource(Start); // distance[],predecessor[]的initialization
int topologicalsort[num_vertex];
GetTopologicalSort(topologicalsort, Start);
for (int i = 0; i < num_vertex; i++) {
int v = topologicalsort[i];
for (std::list<std::pair<int, int>>::iterator itr = AdjList[v].begin();
itr != AdjList[v].end(); itr++) {
Relax(v, (*itr).first, (*itr).second);
}
}
std::cout << "\nprint predecessor:\n";
PrintDataArray(predecessor);
std::cout << "\nprint distance:\n";
PrintDataArray(distance);
}
void Graph_SP::PrintDataArray(std::vector<int> array){
for (int i = 0; i < num_vertex; i++)
std::cout << std::setw(4) << i;
std::cout << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < num_vertex; i++)
std::cout << std::setw(4) << array[i];
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void Graph_SP::PrintIntArray(int *array){
for (int i = 0; i < num_vertex; i++)
std::cout << std::setw(4) << i;
std::cout << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < num_vertex; i++)
std::cout << std::setw(4) << array[i];
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void Graph_SP::InitializeSingleSource(int Start){
distance.resize(num_vertex);
predecessor.resize(num_vertex);
for (int i = 0; i < num_vertex; i++) {
distance[i] = Max_Distance;
predecessor[i] = -1;
}
distance[Start] = 0;
}
void Graph_SP::Relax(int from, int to, int weight){
if (distance[to] > distance[from] + weight) {
distance[to] = distance[from] + weight;
predecessor[to] = from;
}
}
void Graph_SP::AddEdge(int from, int to, int weight){
AdjList[from].push_back(std::make_pair(to,weight));
}
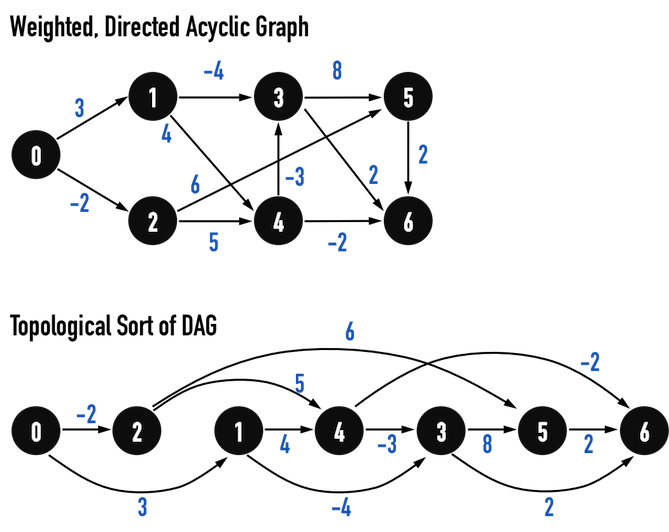
int main(){
Graph_SP g8(7);
g8.AddEdge(0, 1, 3);g8.AddEdge(0, 2, -2);
g8.AddEdge(1, 3, -4);g8.AddEdge(1, 4, 4);
g8.AddEdge(2, 4, 5);g8.AddEdge(2, 5, 6);
g8.AddEdge(3, 5, 8);g8.AddEdge(3, 6, 2);
g8.AddEdge(4, 3, -3);g8.AddEdge(4, 6, -2);
g8.AddEdge(5, 6, 2);
g8.DAG_SP(0); // 以vertex(0)作為起點
return 0;
}
output:
print discover time:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2 12 3 9 4 5
print finish time:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
14 11 13 8 10 7 6
print predecessor:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
-1 0 0 1 2 2 4
print distance:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
0 3 -2 -1 3 4 1
以上結果符合圖四(g)的預期。
若嘗試以vertex(2)作為起點:
int main(){
...
g8.DAG_SP(2);
return 0;
}
output:
print discover time:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
11 12 1 3 2 4 5
print finish time:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
14 13 10 8 9 7 6
print predecessor:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
-1 0 -1 4 2 2 4
print distance:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
100 100 0 2 5 6 3
結果便如圖五,因為從vertex(2)走不到vertex(0)與vertex(1),因此distance[0]與distance[1]仍維持起始值無限大(範例程式將無限大設為\(100\))。

圖五。
以上便是在DAG(directed acyclic graph)中處理Single-Source Shortest Path之演算法之介紹。
同樣地,只要了解:
- Relaxation
- Convergence property
- Path-relaxation property
之概念,即可掌握此演算法的運作邏輯。
下一篇文章將介紹大魔王:Dijkstra's Algorithm,如果讀者熟悉Prim's Algorithm的話,可能會有些幫助。
參考資料:
- Introduction to Algorithms, Ch24
- Fundamentals of Data Structures in C++, Ch6
- Graph: Depth-First Search(DFS,深度優先搜尋)
- Graph: 利用DFS尋找DAG的Topological Sort(拓撲排序)
Shortest Path系列文章
Shortest Path:Intro(簡介)
Single-Source Shortest Path:Bellman-Ford Algorithm
Single-Source Shortest Path:on DAG(directed acyclic graph)
Single-Source Shortest Path:Dijkstra's Algorithm
All-Pairs Shortest Path:Floyd-Warshall Algorithm
回到目錄: