先備知識與注意事項
Queue(佇列)是一種概念性的抽象資料結構,可以分別使用Linked list(連結串列)與Array(陣列)來實作。
本篇文章將介紹Queue的基本概念,並以Linked list實作。
目錄
簡介:Queue
Queue是具有「First-In-First-Out」的資料結構,如同排隊買車票的隊伍即可視為Queue,先進入隊伍的人,可以優先離開隊伍,走向售票窗口買票,而後到的人,就需要等隊伍前面的人都買完票後才能買。
如同普遍認知的排隊隊伍,Queue也具有以下特徵:
- 隊伍有前方(以front表示)以及後方(以back表示)之分。
- 若要進入隊伍(Push),一定是從back進入。
- 若要離開隊伍(Pop),一定是從front離開。
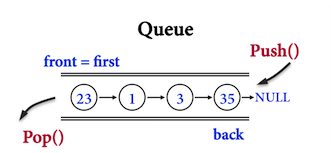
以圖一為例,由front(隊伍前方)和back(隊伍後方)可以判斷,進入隊伍的順序應該是\(23、1、3、35\)。

圖一。
一般的Queue,會有以下幾個處理資料結構的功能,配合圖二:
- Push(data):把資料從Queue的「後面」放進Queue,並更新成新的back。
- 在Queue中新增資料又稱為enqueue。
- Pop:把front所指向的資料從Queue中移除,並更新front。
- 從Queue刪除資料又稱為dequeue。
- getFront:回傳front所指向的資料。
- getBack:回傳back所指向的資料。
- IsEmpty:確認Queue裡是否有資料。
- getSize:回傳Queue裡的資料個數。

圖二。
Queue的應用
因為Queue的「First-In-First-Out」特徵,常用於先到先執行、需要排程(scheduling)的應用:
- 演算法:Breadth-First Search(廣度優先搜尋)與Tree的Level-Order Traversal會用到Queue。
- 作業系統:被多個程式共享的資源(例如CPU、印表機、網站伺服器),一次只能執行一個需求(例如request、interrupt),因此需要有個Queue來安排多個程式的執行順序(例如device queue、job queue),請參考:
以Linked list實作
以Linked list實作Queue非常直覺,如圖三,把每筆資料視為node,並且以pointer前後連結:
- Queue的
Push():在list的「尾巴」新增資料。 - Queue的
Pop():在list的「開頭」刪除資料。
圖三。
和Linked List: 新增資料、刪除資料、反轉介紹的Linked list的差異在於,因為Queue需要記得front和back的資料,所以Linked list除了原先記錄「第一個node」的pointer之外,要再多一個pointer記錄「最後一個node」。
- 有了back pointer後,便能在時間複雜度O(\(1\))完成「在Linked list尾巴新增資料」。
完整的程式範例如下:
// C++ code
#include <iostream>
struct QueueNode{
int data;
QueueNode *next;
QueueNode():data(0),next(0){};
QueueNode(int x):data(x),next(0){};
};
class QueueList{
private:
QueueNode *front;
QueueNode *back;
int size;
public:
QueueList():front(0),back(0),size(0){};
void Push(int x);
void Pop();
bool IsEmpty();
int getFront();
int getBack();
int getSize();
};
void QueueList::Push(int x){
if (IsEmpty()) {
front = new QueueNode(x);
back = front;
size++;
return;
}
QueueNode *newNode = new QueueNode(x);
back->next = newNode;
back = newNode; // update back pointer
size++;
}
void QueueList::Pop(){
if (IsEmpty()) {
std::cout << "Queue is empty.\n";
return;
}
QueueNode *deletenode = front;
front = front->next; // update front pointer
delete deletenode;
deletenode = 0;
size--;
}
int QueueList::getFront(){
if (IsEmpty()) {
std::cout << "Queue is empty.\n";
return -1;
}
return front->data;
}
int QueueList::getBack(){
if (IsEmpty()) {
std::cout << "Queue is empty.\n";
return -1;
}
return back->data;
}
bool QueueList::IsEmpty(){
// return (size == 0);
return ((front && back) == 0);
}
int QueueList::getSize(){
return size;
}
int main(){
QueueList q;
if (q.IsEmpty()) {
std::cout << "Queue is empty.\n";
}
q.Push(24);
std::cout<< "\nAfter push 24: \n";
std::cout << "front: " << q.getFront() << " back: " << q.getBack() << "\n";
q.Push(8);
std::cout<< "\nAfter push 8: \n";
std::cout << "front: " << q.getFront() << " back: " << q.getBack() << "\n";
q.Push(23);
std::cout<< "\nAfter push 23: \n";
std::cout << "front: " << q.getFront() << " back: " << q.getBack() << "\n";
q.Push(13);
std::cout<< "\nAfter push 13: \n";
std::cout << "front: " << q.getFront() << " back: " << q.getBack() << "\n";
q.Pop();
std::cout<< "\nAfter pop the front element: \n";
std::cout << "front: " << q.getFront() << " back: " << q.getBack() << "\n";
q.Push(35);
std::cout<< "\nAfter push 35: \n";
std::cout << "front: " << q.getFront() << " back: " << q.getBack() << "\n";
q.Pop();
std::cout<< "\nAfter pop the front element: \n";
std::cout << "front: " << q.getFront() << " back: " << q.getBack() << "\n";
q.Pop();
std::cout<< "\nAfter pop the front element: \n";
std::cout << "front: " << q.getFront() << " back: " << q.getBack() << "\n";
q.Pop();
std::cout<< "\nAfter pop the front element: \n";
std::cout << "front: " << q.getFront() << " back: " << q.getBack() << "\n";
q.Pop();
std::cout<< "\nAfter pop the front element: \n";
q.Pop();
return 0;
}
output:
```cpp Queue is empty.
After push 24: front: 24 back: 24
After push 8: front: 24 back: 8
After push 23: front: 24 back: 23
After push 13: front: 24 back: 13
After pop the front element: front: 8 back: 13
After push 35: front: 8 back: 35
After pop the front element: front: 23 back: 35
After pop the front element: front: 13 back: 35
After pop the front element: front: 35 back: 35
After pop the front element: Queue is empty.```
以上是Queue的基本介紹。
參考資料:
- Introduction to Algorithms, Ch10
- Fundamentals of Data Structures in C++, Ch3
- Tutorialspoint:Operating System - Process Scheduling。
- Stack Overflow:What are practical applications of Queues?。
- Stack Exchange:Which queue does the long-term scheduler maintain?
- Quora:What are the applications of queues and stacks in C++?
Queue系列文章
Queue: Intro(簡介),並以Linked list實作
Queue: 以Array實作Queue
回到目錄: